-
 colonists accepted the Navigation Acts because the laws told them they could have a place to sell their materials, later they came to not like them.
colonists accepted the Navigation Acts because the laws told them they could have a place to sell their materials, later they came to not like them. -
 a british law, that imposed a tax on molasses, sugar, and rum imported from non-british forgein colonies into the north american colonies
a british law, that imposed a tax on molasses, sugar, and rum imported from non-british forgein colonies into the north american colonies -
 after marching to fort dequesne, washington set up a small fort near by called Fort Necessity. it soon came under attack by french and native american aliies
after marching to fort dequesne, washington set up a small fort near by called Fort Necessity. it soon came under attack by french and native american aliies -
 beginning
beginning
The French had early success and captured several British fort, the The Native Americans worked alongside them
Turning Point
In 1757, William Pitt became prime minister of the British government.Pitt decided to send more trained British troops to fight in North America
End
The Treaty of Paris marked the end of the war. France no longer held power in North America; North America was controlled by Great Britain and Spain. -
 This new tax lowered the tax on molasses imported to the colonies. The idea was that a lower tax:
This new tax lowered the tax on molasses imported to the colonies. The idea was that a lower tax:
It would lower the price, and encourage more people to buy, it Encouraged colonists to stop smuggling,
It also allowed officers to seize accusing smugglers' goods without going to court. -
 the stamp act was to raise money for britian by applying small taxes on all printed materials like newspaper, playing cards, etc.
the stamp act was to raise money for britian by applying small taxes on all printed materials like newspaper, playing cards, etc. -
 the same day as the stamp act. the parliament said they could make laws to make sure american colonies were together
the same day as the stamp act. the parliament said they could make laws to make sure american colonies were together -
 the stamp act was internal while the town shed act is external. they are both very similar, but the citezens were taxed on imported goods like glass, tea, paint, etc.
the stamp act was internal while the town shed act is external. they are both very similar, but the citezens were taxed on imported goods like glass, tea, paint, etc. -
 British soldiers shot and killed 5 colonists during a confrontation. This event created tensions and anger toward British rule.
British soldiers shot and killed 5 colonists during a confrontation. This event created tensions and anger toward British rule. -
 a government for Canada was created, and extended its property all the way south to the Ohio River. the colonies and colonists were trapped there and had no where to go.
a government for Canada was created, and extended its property all the way south to the Ohio River. the colonies and colonists were trapped there and had no where to go. -
 they met in 1774 to address colonial anger against British rule, leading to 'boycott' of British goods and a petition to King George the 3rd
they met in 1774 to address colonial anger against British rule, leading to 'boycott' of British goods and a petition to King George the 3rd -
 Gage took over Boston in 1774 as the British military governor. He aimed to no force British laws. this also increased tensions leading up to the American Revolution
Gage took over Boston in 1774 as the British military governor. He aimed to no force British laws. this also increased tensions leading up to the American Revolution -
 harsh laws passed by Britain in 1774 to punish Massachusetts for the Boston Tea Party. They closed Boston Harbor and restricted colonial self- government.
harsh laws passed by Britain in 1774 to punish Massachusetts for the Boston Tea Party. They closed Boston Harbor and restricted colonial self- government. -
 the quartering act basically states that if a trooper came up to your house you HAD to allow them to stay. at first it was just abandon building, but then it moved to whom evers house
the quartering act basically states that if a trooper came up to your house you HAD to allow them to stay. at first it was just abandon building, but then it moved to whom evers house -
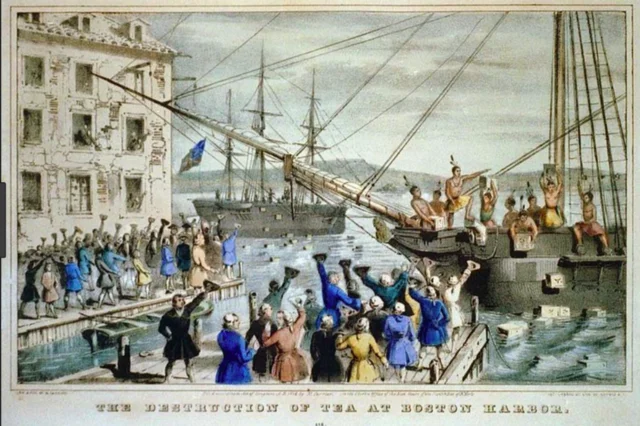 British officials change with a capital offenses had to be tried in another country of England. they protested in Mass.
British officials change with a capital offenses had to be tried in another country of England. they protested in Mass. -
 he rode from Boston to Lexington to warn Samuel Adams and john Handcock that British troops were coming to arrest them and seize colonial weapons. his famous midnight ride helped alert the colonial militia.
he rode from Boston to Lexington to warn Samuel Adams and john Handcock that British troops were coming to arrest them and seize colonial weapons. his famous midnight ride helped alert the colonial militia. -
 On the morning of April 19th, 1775, 70 Minutemen were waiting for the 700 English Redcoats. An unknown shot was fired, and both sides began the battle. It was at the North Bridge that colonists engaged in guerrilla warfare, chasing the British back to Boston. By the time the Redcoats reached Boston, 174 were wounded, 73 were dead, and 18 colonists were wounded.
On the morning of April 19th, 1775, 70 Minutemen were waiting for the 700 English Redcoats. An unknown shot was fired, and both sides began the battle. It was at the North Bridge that colonists engaged in guerrilla warfare, chasing the British back to Boston. By the time the Redcoats reached Boston, 174 were wounded, 73 were dead, and 18 colonists were wounded. -
 German troops were hired by King george the third to help fight against the American colonies. they played a pretty important.
German troops were hired by King george the third to help fight against the American colonies. they played a pretty important. -
 it was captured by the Americans in 1775, which was a big win because they got a bunch of artillery that they later used in other battles.
it was captured by the Americans in 1775, which was a big win because they got a bunch of artillery that they later used in other battles. -
 they managed the colonial war effort and moved towards independence, eventually adopting the Declaration of independence in 1776. it was during this time that they also appointed george washington as the commander for the continental army.
they managed the colonial war effort and moved towards independence, eventually adopting the Declaration of independence in 1776. it was during this time that they also appointed george washington as the commander for the continental army. -
 The militia was low on ammunition, so Colonel Williams Prescott gave the order, "Don't fire until you see the whites of their eyes." Americans were also low on gunpowder to start the battle, so they had to retreat once they ran out of gunpowder. The battle of Bunker Hill was considered a British victory, but at a hefty cost. Just over 1,000 British troops died taking the hill. around 90 militias lost there lives
The militia was low on ammunition, so Colonel Williams Prescott gave the order, "Don't fire until you see the whites of their eyes." Americans were also low on gunpowder to start the battle, so they had to retreat once they ran out of gunpowder. The battle of Bunker Hill was considered a British victory, but at a hefty cost. Just over 1,000 British troops died taking the hill. around 90 militias lost there lives -
 The Olive Branch Petition assured King George 3 that the colonists wanted peace and asked for protection of their rights. The king rejected the petition and prepared for war. He hired more than 30,000 German mercenaries called Hessians to fight alongside British troops.
The Olive Branch Petition assured King George 3 that the colonists wanted peace and asked for protection of their rights. The king rejected the petition and prepared for war. He hired more than 30,000 German mercenaries called Hessians to fight alongside British troops. -

-
 George Washington successfully forced the British to evacuate Boston, after fortifying Dorchester Heights with cannons from Fort Ticonderoga. this was a early victory for the American forces
George Washington successfully forced the British to evacuate Boston, after fortifying Dorchester Heights with cannons from Fort Ticonderoga. this was a early victory for the American forces -
 John Adams, Ben Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Roberts Livingston, and Roger Sherman signed the DOI. Locke expressed that people are born with natural rights to life. liberty and property. that it is the government's job to protect those rights. if a government messes up, it should rightfully be overthrown. the final section proclaims the existence of a new nation.
John Adams, Ben Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Roberts Livingston, and Roger Sherman signed the DOI. Locke expressed that people are born with natural rights to life. liberty and property. that it is the government's job to protect those rights. if a government messes up, it should rightfully be overthrown. the final section proclaims the existence of a new nation.
