-
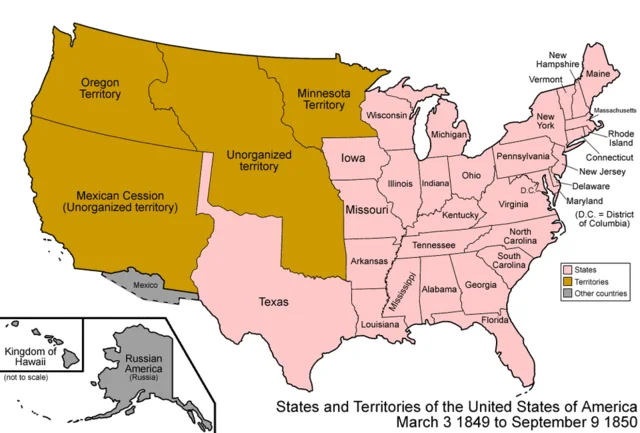 A group of five laws made to calm the fight between the North and South about slavery, especially in new lands gained after the Mexican-American War. It let California join as a free state, allowed people in Utah and New Mexico to vote on slavery, ended the slave trade in Washington, D.C., and made a stricter Fugitive Slave Act. The goal was to keep the country together, but the new law about escaped enslaved people made tensions between the North and South worse.
A group of five laws made to calm the fight between the North and South about slavery, especially in new lands gained after the Mexican-American War. It let California join as a free state, allowed people in Utah and New Mexico to vote on slavery, ended the slave trade in Washington, D.C., and made a stricter Fugitive Slave Act. The goal was to keep the country together, but the new law about escaped enslaved people made tensions between the North and South worse. -
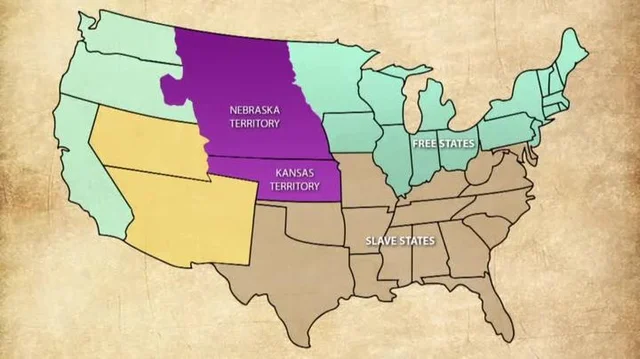 The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska and let the settlers decide if they wanted slavery. It ended the Missouri Compromise, led to violence in “Bleeding Kansas,” and increased tensions before the Civil War.
The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska and let the settlers decide if they wanted slavery. It ended the Missouri Compromise, led to violence in “Bleeding Kansas,” and increased tensions before the Civil War. -
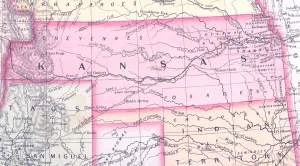 The purpose of the Bleeding Kansas was to organize the territories of Kansas and Nebraska and allow their residents to decide on the legality of slavery via popular sovereignty. The act repealed the Missouri Compromise, which had prohibited slavery in territories north of the latitude line. This reopened the door for slavery's expansion and enraged many in the North.
The purpose of the Bleeding Kansas was to organize the territories of Kansas and Nebraska and allow their residents to decide on the legality of slavery via popular sovereignty. The act repealed the Missouri Compromise, which had prohibited slavery in territories north of the latitude line. This reopened the door for slavery's expansion and enraged many in the North. -
 Dred Scott v. Sandford was a landmark Supreme Court case that ruled that African Americans, whether enslaved or free, could not be American citizens and therefore had no right to sue in federal court. The court declared the Missouri Compromise, that had banned slavery in certain territories, and held that Congress could not prohibit slavery in the territories. This decision intensified sectional tensions and is considered one of the major events leading up to the Civil War.
Dred Scott v. Sandford was a landmark Supreme Court case that ruled that African Americans, whether enslaved or free, could not be American citizens and therefore had no right to sue in federal court. The court declared the Missouri Compromise, that had banned slavery in certain territories, and held that Congress could not prohibit slavery in the territories. This decision intensified sectional tensions and is considered one of the major events leading up to the Civil War. -
 The Lincoln-Douglas debates were a series of seven debates in 1858 between Abraham Lincoln and Stephen A. Douglas for a U.S. Senate seat in Illinois. The debates focused on slavery and its expansion, with Lincoln arguing it was a moral wrong that should be restricted, while Douglas defended popular sovereignty, the idea that settlers should decide the issue for themselves. Although Lincoln lost the election, the debates lead to his presidential victory in 1860.
The Lincoln-Douglas debates were a series of seven debates in 1858 between Abraham Lincoln and Stephen A. Douglas for a U.S. Senate seat in Illinois. The debates focused on slavery and its expansion, with Lincoln arguing it was a moral wrong that should be restricted, while Douglas defended popular sovereignty, the idea that settlers should decide the issue for themselves. Although Lincoln lost the election, the debates lead to his presidential victory in 1860. -
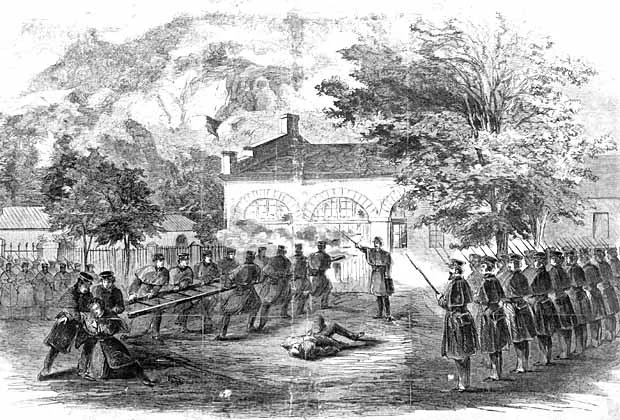 John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry in October 1859 was an attempt by the abolitionist to incite a slave rebellion by seizing the federal armory at Harpers Ferry, Virginia. Brown and his 21 followers were quickly surrounded and defeated by local militia and U.S. Marines led by Colonel Robert E. Lee. The raid, though a failure, intensified sectional tensions over slavery, leading to Brown's execution and fueling Southern fears of slave insurrections.
John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry in October 1859 was an attempt by the abolitionist to incite a slave rebellion by seizing the federal armory at Harpers Ferry, Virginia. Brown and his 21 followers were quickly surrounded and defeated by local militia and U.S. Marines led by Colonel Robert E. Lee. The raid, though a failure, intensified sectional tensions over slavery, leading to Brown's execution and fueling Southern fears of slave insurrections. -
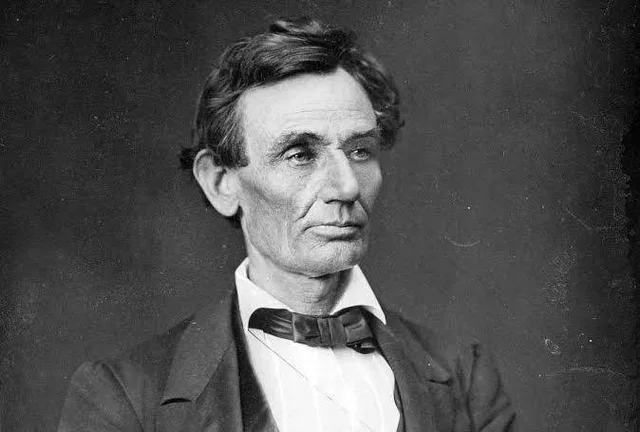 United States presidential election of 1860, American presidential election held on November 6, 1860, in which Republican Abraham Lincoln defeated Southern Democrat John C. Breckinridge, Democrat Stephen A. Douglas, and Constitutional Union candidate John Bell. Lincoln received a majority in the Electoral College, from votes in the Northern states. He prevailed in 18 states, won 180 electoral votes, and received 39.7% of the popular vote. Making him the 16th US. president.
United States presidential election of 1860, American presidential election held on November 6, 1860, in which Republican Abraham Lincoln defeated Southern Democrat John C. Breckinridge, Democrat Stephen A. Douglas, and Constitutional Union candidate John Bell. Lincoln received a majority in the Electoral College, from votes in the Northern states. He prevailed in 18 states, won 180 electoral votes, and received 39.7% of the popular vote. Making him the 16th US. president.